String Operations for IEC
See also: IEC 61131 Language Editor Programming
See also: Project Toolbox for IEC
Topic Menu
Home > View > Project Toolbox > String Operations
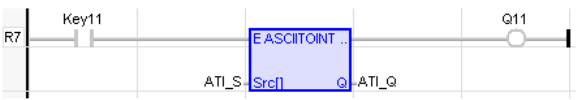
ASCII To INT 
Operator – Perform conversion of ASCII![]() ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. to a INT
ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. to a INT![]() Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767. value.
Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767. value.
Inputs
SRC[ ] : (TYPE : USINT![]() Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - SRC is the array of ASCII value placed at the input.
Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - SRC is the array of ASCII value placed at the input.
Outputs
Q : (TYPE : INT) - The ASCII value converted to Int value.
Remarks
The value at the SRC[] array is separate ASCII value. Ex: SRC[0]- has the first ASCII value, Q – ASCII converted to Int Value.
ST Language
Q := AsciiToInt (Src[]) ;
FBD Language

LD Language
IL Language
Not Available.
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
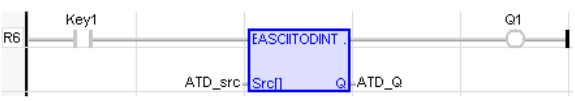
ASCII to DINT 
Operator – Perform conversion of ASCII![]() ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. to a DINT
ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. to a DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. value.
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. value.
Inputs
SRC[ ] : (TYPE :USINT![]() Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - SRC is the array of ASCII value placed at the input.
Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - SRC is the array of ASCII value placed at the input.
Outputs
Q : (TYPE :DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.) - The ASCII value converted to Dint value.
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.) - The ASCII value converted to Dint value.
Remarks
The value at the SRC[] array is separate ASCII value. Ex: SRC[0]- has the first ASCII value, Q – ASCII converted to Dint value.
ST Language
Q := AsciiToDint (Src[]) ;
FBD Language

LD Language
IL Language
Not Available.
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
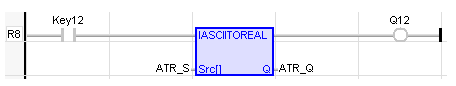
ASCII To REAL 
Operator – Performs conversion of ASCII![]() ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. to a REAL
ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. to a REAL![]() REAL: Single precision floating point value - Real constant expressions must be valid number, and must include a dot ("."). If the user needs to enter a real expression having an integer value, add ".0" at the end of the number. The user can use "F" or "E" separators for specifying the exponent in case of a scientist representation. REAL is the default precision for floating points: such expressions do not need any prefix. value.
REAL: Single precision floating point value - Real constant expressions must be valid number, and must include a dot ("."). If the user needs to enter a real expression having an integer value, add ".0" at the end of the number. The user can use "F" or "E" separators for specifying the exponent in case of a scientist representation. REAL is the default precision for floating points: such expressions do not need any prefix. value.
Inputs
SRC[ ] : (TYPE : USINT![]() Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - SRC is the array of ASCII value placed at the input.
Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - SRC is the array of ASCII value placed at the input.
Outputs
Q : (TYPE : REAL![]() REAL: Single precision floating point value - Real constant expressions must be valid number, and must include a dot ("."). If the user needs to enter a real expression having an integer value, add ".0" at the end of the number. The user can use "F" or "E" separators for specifying the exponent in case of a scientist representation. REAL is the default precision for floating points: such expressions do not need any prefix.) - The ASCII value converted to Real value.
REAL: Single precision floating point value - Real constant expressions must be valid number, and must include a dot ("."). If the user needs to enter a real expression having an integer value, add ".0" at the end of the number. The user can use "F" or "E" separators for specifying the exponent in case of a scientist representation. REAL is the default precision for floating points: such expressions do not need any prefix.) - The ASCII value converted to Real value.
Remarks
The value at the SRC[] array is separate ASCII value. Ex: SRC[0]- has the first ASCII value, Q – ASCII converted to Real Value.
ST Language
Q := AsciiToReal (Src[]) ;
FBD Language

LD Language
IL Language
Not Available.
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
INT to ASCII 
Operator – Perform conversion of INT to ASCII![]() ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. value.
ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. value.
Inputs
SRC: (TYPE : INT![]() Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767.) - This is the Input in Int format for conversion in ASCII value.
Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767.) - This is the Input in Int format for conversion in ASCII value.
DST[ ] : (TYPE : USINT![]() Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - The converted Dint into ASCII is placed in this array of DST. Converted INT to ASCII is terminated with Null character, so DST [] variable must have array size of maximum number of digits + 1.
Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - The converted Dint into ASCII is placed in this array of DST. Converted INT to ASCII is terminated with Null character, so DST [] variable must have array size of maximum number of digits + 1.
Ex: #MAXLEN+1 .
Ex: if maximum number of digits allowed for conversion is 2 then DST [] variable must have array size of 3.
#POINT : (TYPE : INT) - This specifies the place of the point from right of the maximum length allocated.
#MAXLEN: (TYPE : INT) - The maximum number of digits allowed for conversion.
#FILL0: (TYPE : BOOL![]() Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'.) - Fills the vacant place after conversion from Dint to ASCII with zeroes.
Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'.) - Fills the vacant place after conversion from Dint to ASCII with zeroes.
Outputs
Q : (TYPE : BOOL) - The output is TRUE if the Dint value is converted to ASCII successfully.
Remarks
The value at the SRC are separate ASCII value. Ex: DST[0] - has the first ASCII value & so on.
ST Language
Q := IntToAscii (Src, Dst [], #Point, #MaxLen, #Fill0);
FBD Language
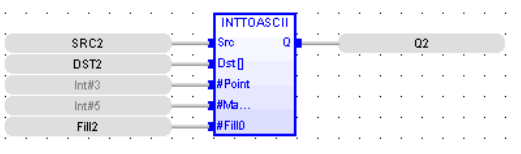
LD Language
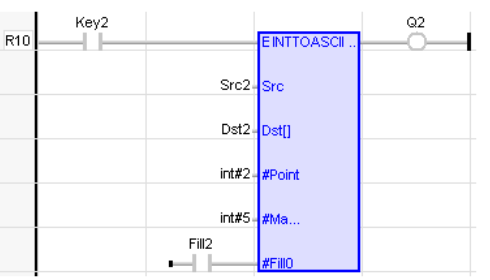
IL Language

Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
DINT to ASCII 
Operator – Perform conversion of DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. to ASCII
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. to ASCII![]() ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. value.
ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. value.
Inputs
SRC: (TYPE : DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.) - This is the Input in Dint format for conversion in ASCII value.
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.) - This is the Input in Dint format for conversion in ASCII value.
DST[ ] : (TYPE : USINT![]() Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - The converted Dint into ASCII is placed in this array of DST. Converted INT to ASCII is terminated with Null character, so DST [] variable must have array size of maximum number of digits + 1
Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - The converted Dint into ASCII is placed in this array of DST. Converted INT to ASCII is terminated with Null character, so DST [] variable must have array size of maximum number of digits + 1
Ex: #MAXLEN+1
Ex: If maximum number of digits allowed for conversion is 2 then DST [] variable must have array size of 3.
#POINT : (TYPE : INT![]() Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767.) - This specifies the place of the point from right of the maximum length allocated.
Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767.) - This specifies the place of the point from right of the maximum length allocated.
#MAXLEN: (TYPE : INT) - The maximum number of digits allowed for conversion.
#FILL0: (TYPE : BOOL![]() Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'.) - Fills the vacant place after conversion from Dint to ASCII with zeroes.
Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'.) - Fills the vacant place after conversion from Dint to ASCII with zeroes.
Outputs
Q : (TYPE : BOOL) - The output is TRUE if the Dint value is converted to ASCII successfully.
Remarks
The value at the SRC are separate ASCII values. x: DST[0] - has the first ASCII value & so on.
ST Language
Q := DintToAscii (Src, Dst[], #Point, #MaxLen, #Fill0);
FBD Language
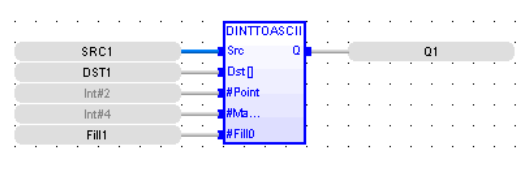
LD Language
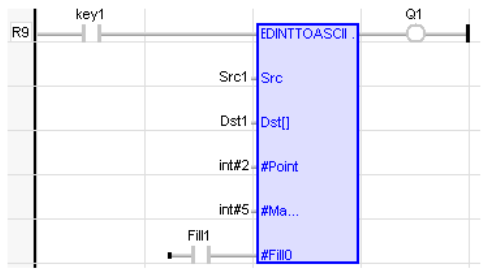
IL Language

Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
Hex To ASCII
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Converts integer to string using hexadecimal![]() A base-16 numbering system which uses the symbols 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F for numeral. basis.
A base-16 numbering system which uses the symbols 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F for numeral. basis.
Inputs
IN : DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Integer value.
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Integer value.
Outputs
Q : STRING![]() String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length. - String representing the integer in hexadecimal format.
String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length. - String representing the integer in hexadecimal format.
Truth Table (examples)
| In | Q |
|---|---|
| 0 | '0' |
| 18 | '12' |
| 160 | 'A0' |
Remarks
In LD language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung. In IL, the input must be loaded in the current result before calling the function.
ST Language
HextoASCIIOP := HEXTOASCII ( HextoASCIIIP );
FBD Language
LD Language
The function is executed only if EN is TRUE.
ENO keeps the same value as EN.

IL Language
Not available.
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
REAL to ASCII 
Operator – Perform conversion of REAL![]() REAL: Single precision floating point value - Real constant expressions must be valid number, and must include a dot ("."). If the user needs to enter a real expression having an integer value, add ".0" at the end of the number. The user can use "F" or "E" separators for specifying the exponent in case of a scientist representation. REAL is the default precision for floating points: such expressions do not need any prefix. to ASCII
REAL: Single precision floating point value - Real constant expressions must be valid number, and must include a dot ("."). If the user needs to enter a real expression having an integer value, add ".0" at the end of the number. The user can use "F" or "E" separators for specifying the exponent in case of a scientist representation. REAL is the default precision for floating points: such expressions do not need any prefix. to ASCII![]() ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. value.
ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. value.
Inputs
SRC: (TYPE : REAL) - This is the Input in Real format for conversion in ASCII value.
DST[ ] : (TYPE : USINT![]() Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - The converted Dint into ASCII is placed in this array of DST. Converted INT to ASCII is terminated with Null character, so DST [] variable must have array size of maximum number of digits + 1
Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - The converted Dint into ASCII is placed in this array of DST. Converted INT to ASCII is terminated with Null character, so DST [] variable must have array size of maximum number of digits + 1
Ex: #MAXLEN+1
Ex: If maximum number of digits allowed for conversion is 2 then DST [] variable must have array size of 3.
#POINT : (TYPE : INT![]() Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767.) - This specifies the place of the point from right of the maximum length allocated.
Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767.) - This specifies the place of the point from right of the maximum length allocated.
#MAXLEN: (TYPE : INT) - The maximum number of digits allowed for conversion.
#FILL0: (TYPE : BOOL![]() Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'.) - Fills the vacant place after conversion from Dint to ASCII with zeroes.
Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'.) - Fills the vacant place after conversion from Dint to ASCII with zeroes.
Outputs
Q : (TYPE : BOOL) - The output is TRUE if the Dint value is converted to ASCII successfully.
Remarks
The value at the SRC are separate ASCII value. Ex: DST[0] - has the first ASCII value & so on.
ST Language
Q := RealToAscii (Src, Dst [], #Point, #MaxLen, #Fill0);
FBD Language
LD Language
IL Language

Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
ASCII To Hex
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Converts string to integer using hexadecimal![]() A base-16 numbering system which uses the symbols 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F for numeral. basis.
A base-16 numbering system which uses the symbols 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F for numeral. basis.
Inputs
Sin: (Type: STRING![]() String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - String representing an integer in hexadecimal format.
String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - String representing an integer in hexadecimal format.
Outputs
Q: (Type: DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.) - Integer represented by the string.
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.) - Integer represented by the string.
Truth table (examples)
| IN | Q |
|---|---|
| " | 0 |
| '12' | 18 |
| 'A0' | 160 |
Remarks
The function is case insensitive. The result is 0 for an empty string. The conversion stops before the first invalid character. In LD language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung. In IL, the input must be loaded in the current result before calling the function.
ST Language
AsciiToHexOP := ASCIITOHEX ( AsciiToHexIP );
FBD Language
LD Language
The function is executed only if EN is TRUE.
ENO keeps the same value as EN.

IL Language
Not Available
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
CHAR ASCII Code
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Get the ASCII![]() ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. code of a character within a string.
ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. code of a character within a string.
Inputs
S1: (Type: STRING![]() String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - Input string
String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - Input string
POS: (Type: DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.) - Position of the character within the string. (The first valid position is 0).
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.) - Position of the character within the string. (The first valid position is 0).
Outputs
Q: (Type: DINT) - ASCII code of the selected character or 0 if position is invalid.
Remarks
In LD language, the input rung (EN) enables the operation, and the output rung keeps the same value as the input rung. In IL language, the first parameter (IN) must be loaded in the current result before calling the function. The other input is the operand of the function.
ST Language
CharcacterASCIIcodeQ := CHARASCIICODE ( CharcacterASCIIcodeIP, CharcacterASCIIcodePos );
FBD Language
LD Language
The function is executed only if EN is TRUE.
ENO is equal to EN.
IL Language
Not available.
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
Array To String
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Copy an array of SINT![]() Short Integer [Data Type SINT] - An 8-bit signed value. Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -128 to +127. to a STRING
Short Integer [Data Type SINT] - An 8-bit signed value. Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -128 to +127. to a STRING![]() String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length..
String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length..
Inputs
SRC []: (Type: SINT) - Source array of SINT small integers
@DST: (Type: STRING) - Destination STRING.
COUNT: (Type: DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.) - Numbers of characters to be copied.
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.) - Numbers of characters to be copied.
Outputs
Q: (Type: DINT) - Number of characters copied.
Remarks
In LD language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung. This function copies the COUNT first elements of the SRC array to the characters of the DST string. The function checks the maximum size of the destination string and adjust the COUNT number if necessary.
ST Language
ArrayToStringQ := ARRAYTOSTRING ( ArrayToStringS, ArrayToStringD, ArrayToStringCount );
FBD Language
LD Language
The function is executed only if EN is TRUE.
ENO keeps the same value as EN.
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
String To Array
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Copies the characters of a STRING![]() String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length. to an array of SINT
String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length. to an array of SINT![]() Short Integer [Data Type SINT] - An 8-bit signed value. Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -128 to +127..
Short Integer [Data Type SINT] - An 8-bit signed value. Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -128 to +127..
Inputs
SRC : STRING - Source STRING.
DST : SINT - Destination array of SINT small integers.
Outputs
Q : DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Number of characters copied.
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Number of characters copied.
Remarks
In LD language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung. In IL, the input must be loaded in the current result before calling the function. This function copies the characters of the SRC string to the first characters of the DST array. The function checks the maximum size destination arrays and reduces the number of copied characters if necessary.
ST Language
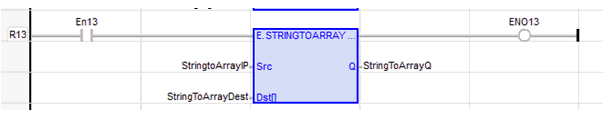
StringToArrayQ := STRINGTOARRAY ( StringtoArrayIP, StringToArrayDest );
FBD Language
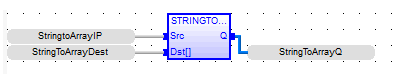
LD Language
The function is executed only if EN is TRUE.
ENO keeps the same value as EN.
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
String To UArray
This block is supported in enhanced IEC only.
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Copies the characters of a STRING![]() String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length. to an array of USINT
String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length. to an array of USINT![]() Short Integer [Data Type SINT] - An 8-bit signed value. Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -128 to +127..
Short Integer [Data Type SINT] - An 8-bit signed value. Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -128 to +127..
Inputs
SRC : STRING - Source STRING.
DST : USINT - Destination array of USINT small integers.
Outputs
Q : DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Number of characters copied.
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Number of characters copied.
Remarks
In LD language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung. In IL, the input must be loaded in the current result before calling the function. This function copies the characters of the SRC string to the first characters of the DST array. The function checks the maximum size destination arrays and reduces the number of copied characters if necessary.
ST Language
StringToArrayQ := STRINGTOUARRAY ( StringtoArrayIP, StringToArrayDest );
FBD Language
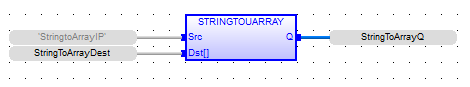
LD Language
The function is executed only if EN is TRUE.
ENO keeps the same value as EN.

Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
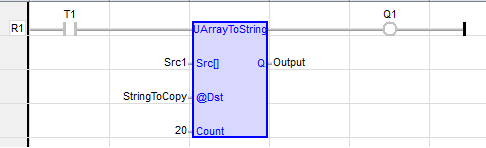
UArray To String
This block is supported in enhanced IEC only.
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Copy an array of USINT![]() Short Integer [Data Type SINT] - An 8-bit signed value. Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -128 to +127. to a STRING
Short Integer [Data Type SINT] - An 8-bit signed value. Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -128 to +127. to a STRING![]() String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length..
String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length..
Inputs
SRC [] : (TYPE: USINT![]() Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.) - Source array of USINT
Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.) - Source array of USINT![]() Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255. small integers.
Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255. small integers.
@DST : (TYPE: STRING![]() String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - Destination STRING
String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - Destination STRING![]() String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length..
String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length..
COUNT : (TYPE: DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.) - Numbers of characters to be copied.
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.) - Numbers of characters to be copied.
Outputs
Q : DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Number of characters copied.
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Number of characters copied.
Remarks
In LD language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung. In IL, the input must be loaded in the current result before calling the function. This function copies the COUNT first elements of the SRC array to the characters of the DST string. The function checks the maximum size destination string and adjust the COUNT number if necessary.
ST Language
Output := UARRAYTOSTRING ( Src1, STRINGTOCOPY, 20);
FBD Language
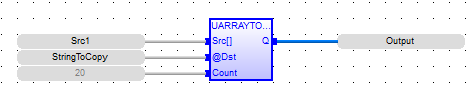
LD Language
The function is executed only if EN is TRUE.
ENO keeps the same value as EN.
NOTE:
On Debug (Watch) Window
As long the data is ASCII, it is displayed correctly, but if there are any numeric values (not ASCII) it is represented as $ followed by the respective numeric value. For example - string has "ABC" followed by numeric 0123 (not ASCII) values, then it displays as ABC$00$01$02$03.
On Graphics
In graphics, we have an ASCII object, which will only display ASCII and not numeric values. For example –
-
If the data is "ABC" followed by 0123 numeric, it will display ABC only.
-
If the data is 0123 numeric followed by "ABC", no string will be displayed.
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
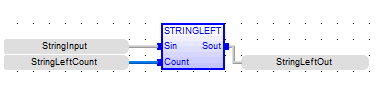
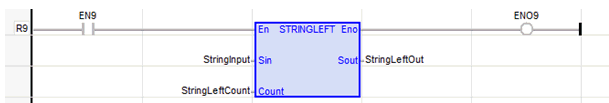
String Left
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Extracts characters of a string on the left.
Inputs
NBC : DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Number of characters to extract.
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Number of characters to extract.
Outputs
Q : STRING - String containing the first NBC characters of IN.
Remarks
In LD language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung. In IL, the first input (the string) must be loaded in the current result before calling the function. The second argument is the operand of the function.
ST language
StringLeftOut := STRINGLEFT ( StringInput, StringLeftCount );
FBD Language
LD Language
The function is executed only if EN is TRUE.
ENO keeps the same value as EN.
IL Language
Not available.
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
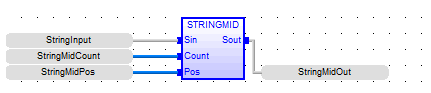
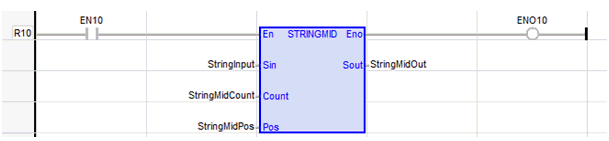
String Mid
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Extracts characters of a string at any position.
Inputs
NBC : DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Number of characters to extract.
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Number of characters to extract.
POS : DINT - Position of the first character to extract (first character of IN is at position 0).
Outputs
Q : STRING - String containing the first NBC characters of IN.
Remarks
The first valid position is 0. In LD language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung. In IL, the first input (the string) must be loaded in the current result before calling the function. Other argument are operands of the function, separated by commas.
ST Language
StringMidOut := STRINGMID ( StringInput, StringMidCount, StringMidPos )
FBD Language
LD Language
The function is executed only if EN is TRUE.
ENO keeps the same value as EN.
IL Language
O1: LD IN
MID NBC, POS
ST Q
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
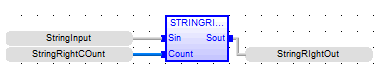
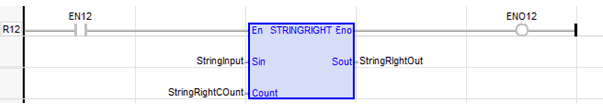
String Right
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Extracts characters of a string on the right.
Inputs
IN : STRING - Character string.
NBC : DINT - Number of characters to extract.
Outputs
Q : STRING - String containing the last NBC characters of IN.
Remarks
In LD language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung. In IL, the first input (the string) must be loaded in the current result before calling the function. The second argument is the operand of the function.
ST Language
StringRIghtOut := STRINGRIGHT ( StringInput, StringRightCOunt );
FBD Language
LD Language
The function is executed only if EN is TRUE.
ENO keeps the same value as EN.
IL Language

Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
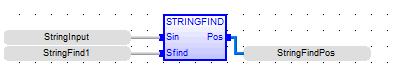
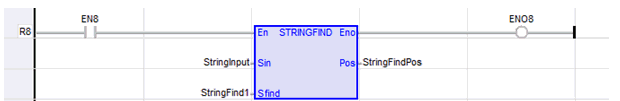
String Find
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Finds position of characters in a string.
Inputs
STR : STRING - String containing searched characters.
Outputs
POS : DINT - Position of the first character of STR in IN, or 0 if not found.
Remarks
The first valid character position is 1. A return value of 0 means that the STR string has not been found. Search is case sensitive. In LD language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung. In IL, the first input (the string) must be loaded in the current result before calling the function. The second argument is the operand of the function.
ST Language
StringFindPos := STRINGFIND ( StringInput, StringFind1 );
FBD Language
LD Language
IL Language
Not available.
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
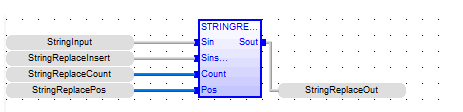
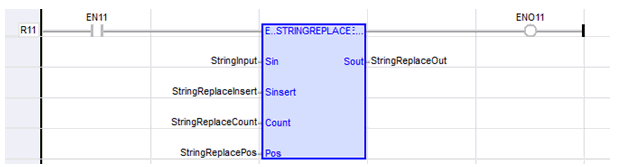
String Replace
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Replaces characters in a string.
Inputs
STR : STRING - String containing the characters to be inserted in place of NDEL removed characters.
NDEL : DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Number of characters to be deleted before insertion of STR.
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Number of characters to be deleted before insertion of STR.
POS : DINT - Position where characters are replaced (first character position is 0).
Outputs
Q : STRING Modified string.
Remarks
The first valid character position is 0. In LD language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung. In IL, the first input (the string) must be loaded in the current result before calling the function. Other arguments are operands of the function, separated by commas.
ST Language
StringReplaceOut := STRINGREPLACE ( StringInput, StringReplaceInsert, StringReplaceCount, StringReplacePos );
FBD Language
LD Language
The function is executed only if EN is TRUE.
ENO keeps the same value as EN.
IL Language

Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
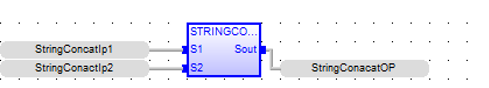
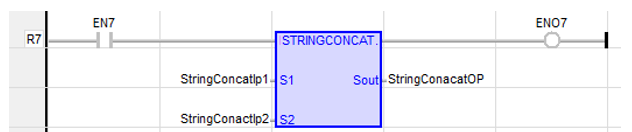
String Concatenate
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Concatenate or link together in strings.
Inputs
S1: (Type: STRING![]() String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - Any string variable or constant expression.
String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - Any string variable or constant expression.
S2: (Type: STRING) - Any string variable or constant expression.
Outputs
Sout: (Type: STRING) - Concatenation of all inputs.
Remarks
In FBD or LD language, the block may have up to 16 inputs. In IL or ST, the function accepts a variable number of inputs (at least 2). NOTE: The user can also use the "+" operator to concatenate strings.
ST Language
StringConacatOP := STRINGCONCAT ( StringConcatIp1, StringConactIp2 );
FBD Language
LD Language
IL Language
Not available.
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
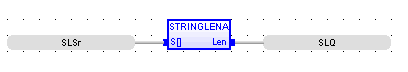
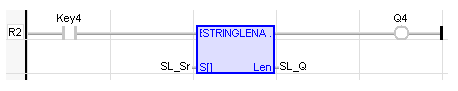
Variable String Length
Operator – Length of a given input string.
Inputs
S[ ] : (TYPE : USINT![]() Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - S is the source string ASCII
Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - S is the source string ASCII![]() ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. value.
ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. value.
Outputs
LEN : (TYPE :INT![]() Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767.) - Length of the elements in array S.
Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767.) - Length of the elements in array S.
Remarks
En is the Enable input & Eno is the enable output. En & Eno will be in same state.
ST Language
LEN := StringLen (S[]);
FBD Language
LD Language
IL Language
Not Available.
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
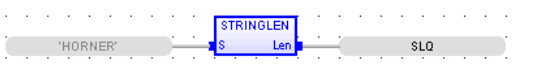
Constant String Length
Operator – Length of a given input string.
Inputs
S : (TYPE : STRING![]() String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - S is the string in ASCII
String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - S is the string in ASCII![]() ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. value.
ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. value.
Outputs
LEN : (TYPE :INT![]() Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767.) - Length of the elements in String.
Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767.) - Length of the elements in String.
ST Language
LEN:= StringLen ( 'Test' );
FBD Language
LD Language

IL Language

Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
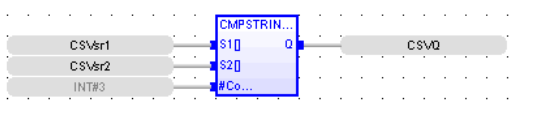
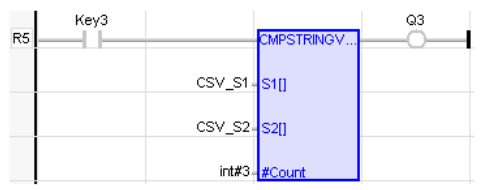
Compare Strings
Operator – Perform comparison of String variables.
Inputs
S1[ ] : (TYPE : USINT![]() Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - S1 is the array of ASCII values placed to compare with the input at S2.
Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - S1 is the array of ASCII values placed to compare with the input at S2.
S2[ ] : (TYPE : USINT[]) - S2 is the array of ASCII values to which input S1 is compared with.
#COUNT : (TYPE : INT![]() Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767.) - The number of characters to be compared.
Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767.) - The number of characters to be compared.
Outputs
Q : (TYPE :BOOL) - Output goes high if the input ASCII values are equal for a given count.
Remarks
Each element of array S1[] is compared with each element of array S2[]. Ex: S1[0] is compared with value at S2[0], till the given count at #COUNT input.
ST Language
Q := CmpStringVar (S1[], S2[], #Count) ;
FBD Language
LD Language
IL Language
Not Available.
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
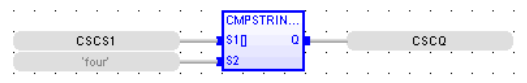
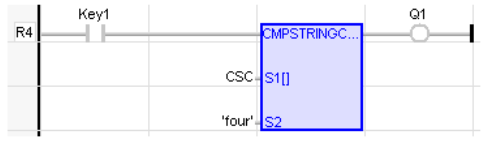
Compare String with Constant Data
Operator – Perform comparison of String with a constant.
Inputs
S1[ ] : (TYPE : USIN![]() Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.T[]) - S1 is the array of ASCII values placed to compare with the input at S2.
Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.T[]) - S1 is the array of ASCII values placed to compare with the input at S2.
S2: (TYPE : STRING![]() String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - S2 is the string to which input S1 is compared.
String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - S2 is the string to which input S1 is compared.
Outputs
Q : (TYPE : BOOL![]() Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'.) - Output goes high if the inputs are equal.
Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'.) - Output goes high if the inputs are equal.
Remarks
The value at the S1[] array is character wise ASCII value. Ex: S1[0]- has the first alphabet’s ASCII value, S1[1]- has the second alphabet’s ASCII value & so on.
ST Language
Q: = CmpStringConst (S1[] , S2) ;
FBD Language
LD Language
IL Language
Not Available.
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
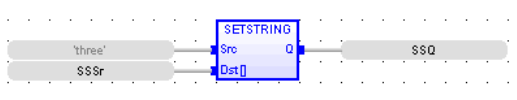
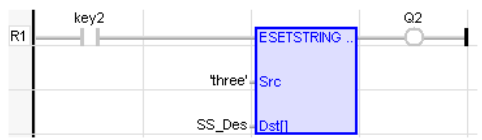
Set String
Operator – Sets the ASCII![]() ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. value of the source at the destination array.
ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII-coded characters are single-byte values in the range of 0 (zero) to 127. Codes in the range 128 to 255 are not defined by the ASCII standard, but rather by the equipment manufacturer. value of the source at the destination array.
Inputs
SRC : (TYPE : STRING![]() String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - SRC is the source string.
String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - SRC is the source string.
DST[ ] : (TYPE :USINT![]() Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - DST is the converted ASCII value.
Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.[]) - DST is the converted ASCII value.
Outputs
Q : (TYPE :BOOL![]() Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'.) - Output goes high if the SetString is successful.
Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'.) - Output goes high if the SetString is successful.
Remarks
The value at the DST[] array is character wise ASCII value. Ex: DST[0]- has the first alphabet’s ASCII value, DST[1]- has the second alphabet’s ASCII value & so on.
ST Language
Q := SetString(Src, Dst[]);
FBD Language
LD Language
IL Language

Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
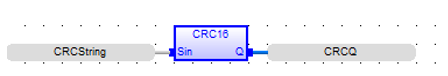
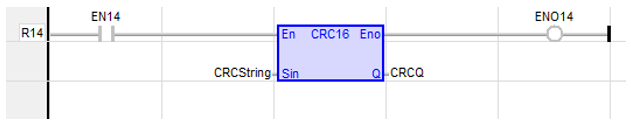
Calculate CRC16
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Calculates a CRC16 on the characters of a string.
Inputs
Sin: (Type: STRING![]() String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - Input character string.
String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.) - Input character string.
Outputs
Q : DINT CRC16 calculated on all the characters of the string.
Remarks
In LD language, the input rung (EN) enables the operation, and the output rung keeps the same value as the input rung. In IL language, the input parameter (IN) must be loaded in the current result before calling the function. The function calculates a MODBUS CRC16, initialized at 16#FFFF value.
ST Language
CRCQ := CRC16 ( CRCString );
FBD Language
LD Language
The function is executed only if EN is TRUE.
ENO is equal to EN.
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
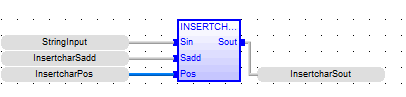
Insert CHARS
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Inserts characters in a string.
Inputs
STR : STRING - String containing characters to be inserted.
POS : DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Position of the first inserted character (first character position is 0).
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Position of the first inserted character (first character position is 0).
Outputs
Q : STRING - Modified string.
Remarks
The first valid character position is 0. In LD language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung. In IL, the first input (the string) must be loaded in the current result before calling the function. Other arguments are operands of the function, separated by commas.
ST Language
InsertcharSout := INSERTCHARS ( StringInput, InsertcharSadd, InsertcharPos );
FBD Language
LD Language
The function is executed only if EN is TRUE.
ENO keeps the same value as EN.
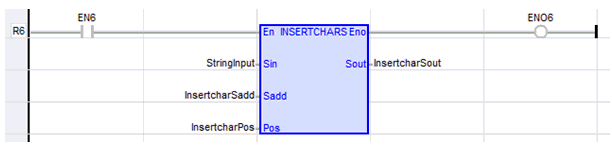
IL Language

Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC
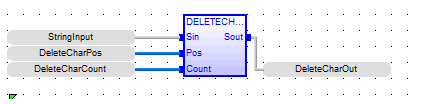
Delete CHARS
See also: Enhanced IEC 61131 Guide
Function - Delete characters in a string.
Inputs
NBC : DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Number of characters to be deleted.
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647. - Number of characters to be deleted.
POS : DINT - Position of the first deleted character (first character position is 0).
Outputs
Q : STRING Modified string.
Remarks
The first valid character position is 0. In LD language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung. In IL, the first input (the string) must be loaded in the current result before calling the function. Other arguments are operands of the function, separated by commas.
ST Language
DeleteCharOut := DELETECHARS ( StringInput, DeleteCharPos, DeleteCharCount );
FBD Language
LD Language
The function is executed only if EN is TRUE.
ENO keeps the same value as EN.
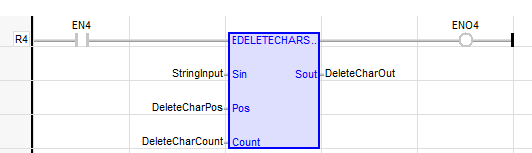
Return to the Top: String Operations for IEC