Math - Standard for IEC
See also: IEC 61131 Language Editor Programming
See also: Project Toolbox for IEC
Topic Menu
Add 
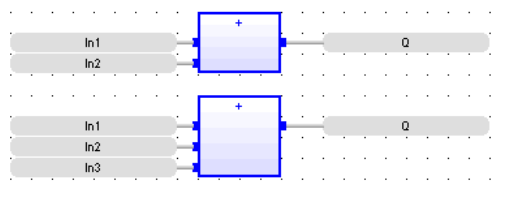
Operator - Performs an addition of all inputs.
Inputs
IN1 : ANY (numeric) First input
IN2 : ANY (numeric) Second input
Outputs
Q : ANY Result: IN1 + IN2
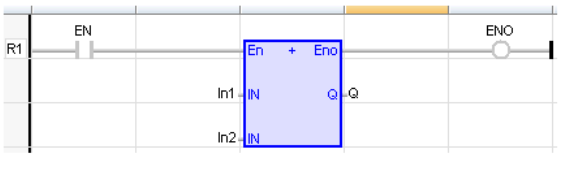
Remarks - All inputs and the output must have the same type. In FBD language, the block may have up to 255 inputs. In LD language, the EN signal enables the operation, and the ENO keeps the same value as the EN. In IL language, the ADD instruction performs an addition between the current result and the operand. The current result and the operand must have the same type.
ST Language
Q := IN1 + IN2;
FBD Language
(* the block may have up to 255 inputs *)
LD Language
(* The addition is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO is equal to EN *)
IL Language

Return to the Top: Math - Standard for IEC
Subtract 
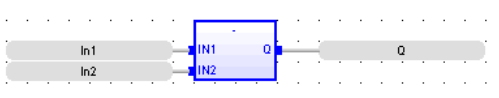
Operator - Performs a subtraction of inputs.
Inputs
IN1 : ANY (numeric) / TIME First input
IN2 : ANY (numeric) / TIME Second input
Outputs
Q : ANY_NUM / TIME Result: IN1 - IN2
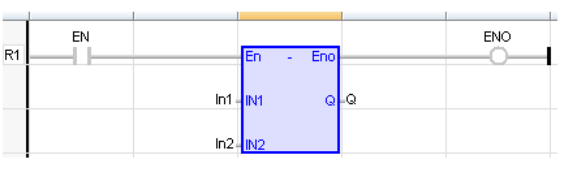
Remarks - All inputs and the output must have the same type. In LD language, the EN signal enables the operation, and the ENO keeps the same value as the EN. In IL language, the SUB instruction performs a subtraction between the current result and the operand. The current result and the operand must have the same type.
ST Language
Q := IN1 - IN2;
FBD Language
LD Language
(* The subtraction is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO is equal to EN *)
IL Language

Return to the Top: Math - Standard for IEC
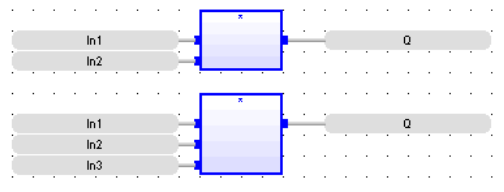
Multiply 
Operator - Performs a multiplication of all inputs.
Inputs
IN1 : ANY (numeric) First input
IN2 : ANY (numeric) Second input
Outputs
Q : ANY_NUM Result: IN1 * IN2
Remarks - All inputs and the output must have the same type. In FBD language, the block may have up to 255 inputs. In LD language, the EN signal enables the operation, and the ENO keeps the same value as the EN. In IL language, the MUL instruction performs a multiplication between the current result and the operand. The current result and the operand must have the same type.
ST Language
Q := IN1 * IN2;
FBD Language
(* the block may have up to 255 inputs *)
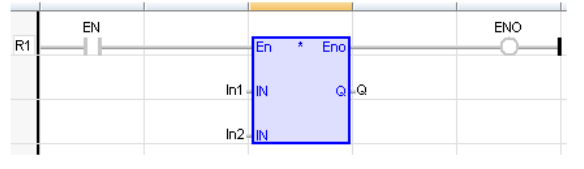
LD Language
(* The multiplication is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO is equal to EN *)
IL Language

Return to the Top: Math - Standard for IEC
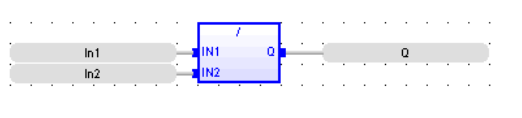
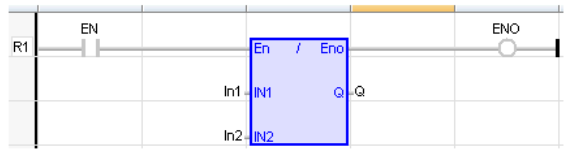
Divide 
Operator - Performs a division of inputs.
Inputs
IN1 : ANY (numeric) First input
IN2 : ANY (numeric) Second input
Outputs
Q : ANY_NUM Result: IN1 / IN2
Remarks - All inputs and the output must have the same type. In LD language, the input rung EN signal enables the operation, and the ENO keeps the same value as the EN. In IL language, the DIV instruction performs a division between the current result and the operand. The current result and the operand must have the same type.
ST Language
Q := IN1 / IN2;
FBD Language
LD Language
(* The division is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO is equal to EN *)
IL Language

Return to the Top: Math - Standard for IEC
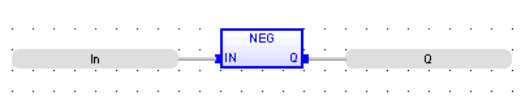
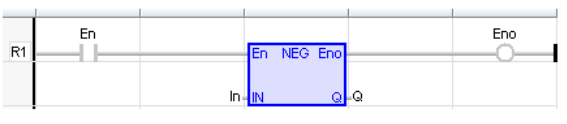
Negation
Operator - Performs an integer negation of the input.
Inputs
Outputs
Q : DINT Integer negation of the input
Truth table (examples)
| IN | Q |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | -1 |
| -123 | 123 |
Remarks - In FBD and LD language, the block "NEG" can be used. In LD language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung. This feature is not available in IL language. In ST language, "-" can be followed by a complex Boolean expression between parenthesis.
ST Language
Q := -IN;
Q := - (IN1 + IN2);
FBD Language
LD Language
(* The negation is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO keeps the same value as EN *)
IL Language

Return to the Top: Math - Standard for IEC
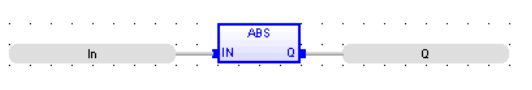
Absolute Value 
Function - Returns the absolute value of the input.
Inputs
Outputs
Q : REAL/LREAL Result: absolute value of IN
Remarks - In LD language, the operation is executed only if the EN is TRUE. The ENO keeps the same value as the EN. In IL, the input must be loaded in the current result before calling the function.
ST Language
Q := ABS (IN);
FBD Language
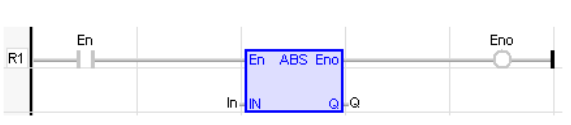
LD Language
(* The function is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO keeps the same value as EN *)
IL Language

Return to the Top: Math - Standard for IEC
Square Root 
Function - Calculates the square root of the input.
Inputs
Outputs
Q : REAL Result: square root of IN
Remarks - In LD language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung. In IL, the input must be loaded in the current result before calling the function.
ST Language
Q := SQRT (IN) ;
FBD Language

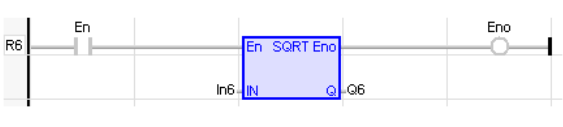
LD Language
(* The function is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO keeps the same value as EN *)
IL Language

Return to the Top: Math - Standard for IEC
Integer Scaling  The process of changing a quantity from one notation to another.
The process of changing a quantity from one notation to another.
Operator – This function scales the input to the specified range.
Inputs
IN: The input which needs to be scaled to a specified range. (TYPE : INT)
MinIN: The minimum value of the input which has a defined scale. (TYPE : INT)
MaxIN: The maximum value of the input which has a defined scale. (TYPE : INT)
MinQ: The minimum value to which the input needs to be scaled. (TYPE : INT)
MaxQ: The maximum value to which the input needs to be scaled. (TYPE : INT)
Outputs
Q : The scaled output in the range of MinQ & MaxQ specified. (TYPE : INT)
Remarks
Cases often arise when numbers on one scale need to be translated to another scale.
The MinIN and MaxIN ranges indicated the expected or nominal values that the input can be expected to attain. This is the range of values that corresponds to the expected output range.
The MinQ and MaxQ Ranges indicate the range of value that the input signal is converted to.
ST Language
Q := ScaleInt (IN, MinIN, MaxIN, MinQ, MaxQ) ;
FBD Language
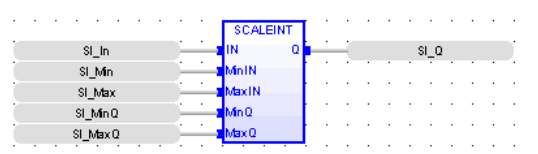
LD Language
IL Language

Return to the Top: Math - Standard for IEC
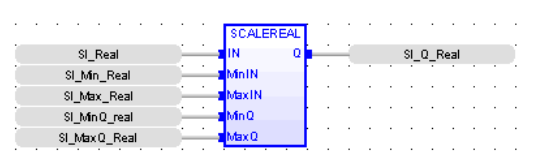
Real Scaling  The process of changing a quantity from one notation to another.
The process of changing a quantity from one notation to another.
Operator – This function scales the input to the range specified.
Inputs
IN: (TYPE : REAL) - The input which needs to be scaled to a specified range.
MinIN: (TYPE : REAL) - The minimum value of the input which has a defined scale.
MaxIN: (TYPE : REAL) - The maximum value of the input which has a defined scale.
MinQ: (TYPE : REAL) - The minimum value to which the input needs to be scaled.
MaxQ: (TYPE : REAL) - The maximum value to which the input needs to be scaled.
Outputs
Q : The scaled output in the range of MinQ & MaxQ specified. (TYPE : REAL)
Remarks
Cases often arise when numbers on one scale need to be translated to another scale.
The MinIN and MaxIN Ranges indicate the expected or nominal values that the input can be expected to attain.
The MinQ and MaxQ Ranges indicate the range of value that the input signal is converted to.
ST Language
Q := ScaleReal (IN, MinIN, MaxIN, MinQ, MaxQ) ;
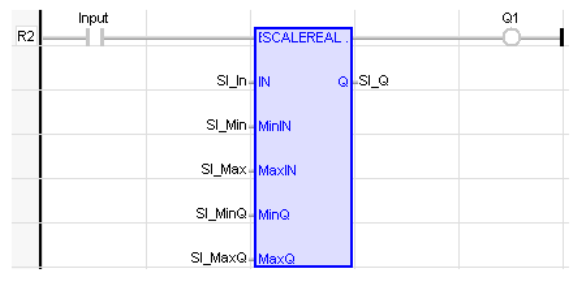
FBD Language
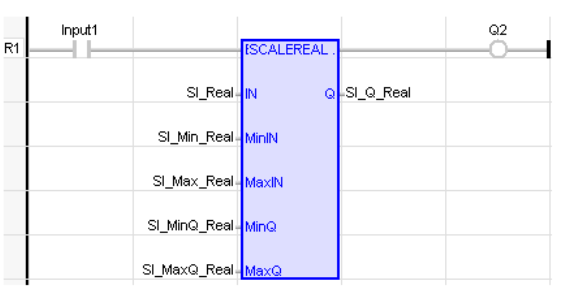
LD Language
IL Language

Return to the Top: Math - Standard for IEC
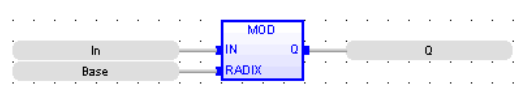
Modulo
MOD
Function - Calculation of modulo.
Inputs
BASE : DINT Base of the modulo
Outputs
Q : DINT Modulo: rest of the integer division (IN / BASE)
Remarks - In LD language, the input rung EN signal enables the operation, and the ENO keeps the state of the EN. In IL language, the first input must be loaded before the function call. The second input is the operand of the function.
Note: Supported data types - DINT, REAL and LREAL (LREAL - supported in EIEC only)
ST Language
Q := MOD (IN, BASE) ;
FBD Language
LD Language
(* The comparison is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO has the same value as EN *)
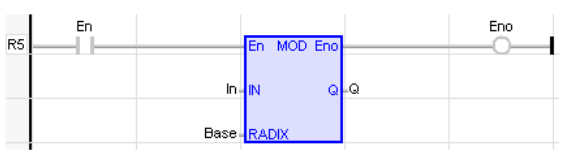
IL Language

Return to the Top: Math - Standard for IEC