Counter Operations for IEC
See also: IEC 61131 Language Editor Programming
See also: Project Toolbox for IEC
Topic Menu
The following Counter Operations are supported only in Enhanced IEC
• Retentive Up Counter
• Retentive Down Counter
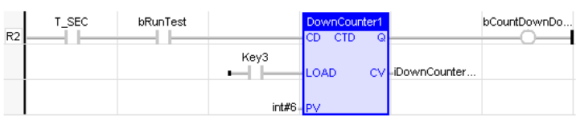
Down Counter
CTD
Function - Down counter.
Inputs
CD : BOOL![]() Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'. - Enable counting. Counter is decreased on each call when CD is TRUE
Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'. - Enable counting. Counter is decreased on each call when CD is TRUE
LOAD : BOOL - Re-load command. Counter is set to PV when called with LOAD to TRUE
PV : INT![]() Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767. - Programmed maximum value
Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767. - Programmed maximum value
Outputs
Q : BOOL TRUE - when counter is empty, i.e. when CV = 0
CV : INT - Current value of the counter
Remarks - The counter is empty (CV = 0) when the application starts. Counter is set to PV when called with LOAD to TRUE. The counter does not include a pulse detection for CD input. Use R_TRIG or F_TRIG function block for counting pulses of CD input signal. In LD language, CD is the input rung. The output rung is the Q output.
ST Language
(* MyCounter is a declared instance of CTD function block *)
MyCounter (CD, LOAD, PV);
Q := MyCounter.Q;
CV := MyCounter.CV;
FBD Language
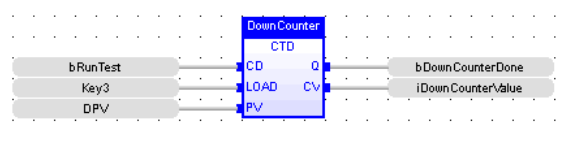
LD Language
IL Language
(* MyCounter is a declared instance of CTD function block *)

Return to the Top: Counter Operations for IEC
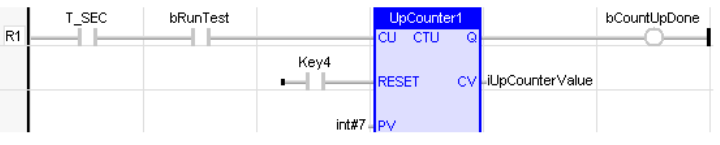
Up Counter
CTU
Function - Up counter
Inputs
CU : BOOL - Enable counting. Counter is increased on each call when CU is TRUE
RESET : BOOL - Reset command. Counter is reset to 0 when called with RESET to TRUE
PV : INT - Programmed maximum value
Outputs
Q : BOOL TRUE - when counter is full, i.e. when CV = PV
CV : INT - Current value of the counter
Remarks - The counter is empty (CV = 0) when the application starts. The counter does not include a pulse detection for CU input. Use R_TRIG or F_TRIG function block for counting pulses of CU input signal. In LD language, CU is the input rung. The output rung is the Q output.
ST Language
(* MyCounter is a declared instance of CTU function block *)
MyCounter (CU, RESET, PV);
Q := MyCounter.Q;
CV := MyCounter.CV;
FBD Language
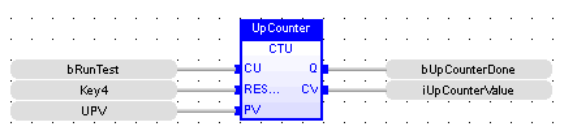
LD Language
IL Language
(* MyCounter is a declared instance of CTU function block *)

Return to the Top: Counter Operations for IEC
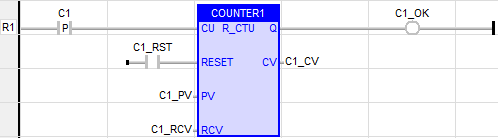
Retentive Up Counter
Also called as: R_CTU -(16-bit Resolution)
Inputs
CU (Count Up): - BOOL
RESET: - BOOL
PV (Preset Value): - INT
RCV (Retained Current Value): - INT
Outputs
Q (output): - BOOL
CV (Current Value): - INT
LD Language
IL Language

ST Language

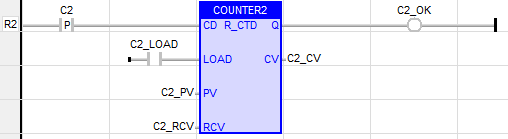
Retentive Down Counter
Also called as: R_CTD -(16-bit Resolution)
Inputs
CD (Count Down): - BOOL
LOAD: - BOOL
PV (Preset Value): - INT
RCV (Retained Current Value): - INT
Outputs
Q (output): - BOOL
CV (Current Value): - INT
LD Language
IL Language

ST Language
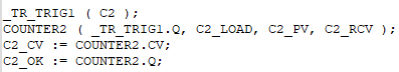
Functional Description
A Retentive Counter functions similarly to a standard counter, with one key enhancement:
The accumulated count value is preserved when –
-
The input signal turns OFF
-
The controller restarts
-
The controller transitions between operating modes (IDLE → RUN)
A Retentive Counter resets only when an explicit Reset signal is applied.
Retention of CV (Current Value) Using RCV (Retained Current Value)
The Retentive Counter uses an auxiliary variable, RCV (Retained Current Value), to preserve the accumulated count across power cycles and operating mode transitions.
Key Requirements
-
RCV is a Read-Only variable.
-
The RCV variable must be defined as a Retain variable in the Retain Variable window.
-
When RCV is configured as a Retain variable, the CV value is retained after:
-
A full power cycle
-
A transition from IDLE → RUN
-
If the RCV variable is created in the Global Variable window, the CV value will not be retained after a restart or mode change
.
PV (Preset Value), CV (Current Value), and RCV (Retained Current Value) Requirements
RCV Variable
-
Must be created as a Retain variable.
-
Stores the last valid accumulated value of the counter.
-
When the device restarts or transitions from IDLE → RUN:
-
The CV register is initialized to zero.
-
The system automatically transfers the stored RCV value into CV, restoring the last known count.
-
CV Variable
-
Can be created in either Global or Retain variable windows.
-
CV retention depends entirely on the configuration of the RCV variable.
-
If RCV is Retain → CV is restored.
-
If RCV is Global → CV is not restored.
-
PV Variable (Preset Value)
-
If the preset value must persist after a power cycle or mode transition, the PV variable should be created in the Retain Variable window.
-
If PV is Global, it will reset to its default value after restart.
CV Restoration Mechanism
During a device restart or when transitioning from IDLE → RUN –
-
CV is initialized to zero by the system.
-
The controller checks for an associated RCV Retain variable.
-
If RCV exists as a Retain variable:
-
The stored RCV value is automatically restored into CV.
-
-
Counter operation resumes from the restored CV value, rather than starting from zero.
This ensures that counting continues seamlessly across operational interruptions.
Return to the Top: Counter Operations for IEC