Conversion Operations for IEC
See also: IEC 61131 Language Editor Programming
See also: Project Toolbox for IEC
Topic Menu
Convert to Boolean Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'.
Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'.
Any to Bool
Operator - Converts the input into Boolean value.
Inputs
IN : ANY Input value
Outputs
Q : BOOL Value converted to Boolean
Remarks - For DINT![]() Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647., REAL
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647., REAL![]() These numbers use IEEE 754-1985 format to store numbers in following ranges.
32-bit single-precision floating point (REAL) – -3.40282E+38 to +3.40282E+38
64-bit double-precision floating point (LREAL) – -1.79769E+308 to +1.7976E+308
Floating Point refers to both REAL and LREAL data types. and TIME
These numbers use IEEE 754-1985 format to store numbers in following ranges.
32-bit single-precision floating point (REAL) – -3.40282E+38 to +3.40282E+38
64-bit double-precision floating point (LREAL) – -1.79769E+308 to +1.7976E+308
Floating Point refers to both REAL and LREAL data types. and TIME![]() TIME: Time of day - Time constant expressions represent durations that must be less than 24 hours. Expressions must be prefixed by either "TIME#" or "T#". They are expressed as a number of hours followed by "h", a number of minutes followed by "m", a number of seconds followed by "s", and a number of milliseconds followed by "ms". The order of units (hour, minutes, seconds, milliseconds) must be respected. The user cannot insert blank characters in the time expression. There must be at least one valid unit letter in the expression. input data types, the result is FALSE if the input is 0. The result is TRUE in all other cases. For STRING inputs, the output is TRUE if the input string is not empty, and FALSE if the string is empty. In LD language, the conversion is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung is the result of the conversion. In IL Language, the ANY_TO_BOOL function converts the current result.
TIME: Time of day - Time constant expressions represent durations that must be less than 24 hours. Expressions must be prefixed by either "TIME#" or "T#". They are expressed as a number of hours followed by "h", a number of minutes followed by "m", a number of seconds followed by "s", and a number of milliseconds followed by "ms". The order of units (hour, minutes, seconds, milliseconds) must be respected. The user cannot insert blank characters in the time expression. There must be at least one valid unit letter in the expression. input data types, the result is FALSE if the input is 0. The result is TRUE in all other cases. For STRING inputs, the output is TRUE if the input string is not empty, and FALSE if the string is empty. In LD language, the conversion is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE. The output rung is the result of the conversion. In IL Language, the ANY_TO_BOOL function converts the current result.
ST Language
Q := ANY_TO_BOOL (IN) ;
FBD Language
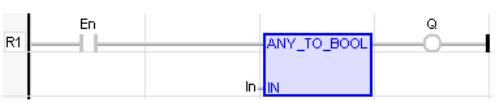
LD Language
(* The conversion is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* The output rung is the result of the conversion *)
(* The output rung is FALSE if the EN is FALSE *)
IL Language

Return to the Top: Conversion Operations for IEC
Convert to SINT8
Any To SINT Short Integer [Data Type SINT] - An 8-bit signed value. Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -128 to +127.
Short Integer [Data Type SINT] - An 8-bit signed value. Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -128 to +127.
Operator - Converts the input into a small (8 bit) integer value.
Inputs
IN : ANY Input value
Outputs
Q : SINT Value converted to a small (8 bit) integer
Remarks - For BOOL input data types, the output is 0 or 1. For REAL input data type, the output is the integer part of the input real. For TIME input data types, the result is the number of milliseconds. For STRING inputs, the output is the number represented by the string, or 0 if the string does not represent a valid number. In LD language, the conversion is executed only if the EN is TRUE. The ENO keeps the same value as the EN. In IL Language, the ANY_TO_SINT function converts the current result.
ST Language
Q := ANY_TO_SINT (IN) ;
FBD Language
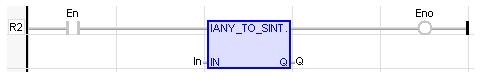
LD Language
(* The conversion is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO keeps the same value as EN *)
IL Language

Return to the Top: Conversion Operations for IEC
Convert to USINT8
Any To USINT Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.
Unsigned Short Integer - [Data Type USINT] - An 8-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Short Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 255.
Operator - Converts the input into a Unsigned Small (8 bit) Integer value.
Inputs
IN : ANY Input value
Outputs
Q : USINT Value converted to a unsigned small (8 bit) integer
Remarks - For BOOL input data types, the output is 0 or 1. For REAL input data type, the output is the integer part of the input real. For TIME input data types, the result is the number of milliseconds. For STRING inputs, the output is the number represented by the string, or 0 if the string does not represent a valid number. In LD language, the conversion is executed only if the EN is TRUE. The ENO keeps the same value as the EN. In IL Language, the ANY_TO_USINT function converts the current result.
ST Language
Q := ANY_TO_USINT (IN) ;
FBD Language
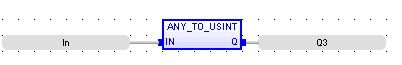
LD Language
(* The conversion is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO keeps the same value as EN *)

IL Language
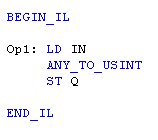
Return to the Top: Conversion Operations for IEC
Convert to INT16
ANY TO INT  Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767.
Integer - [Data Type INT] - A 16-bit signed value. Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -32,768 to +32,767.
Operator - Converts the input into 16 bit integer value.
Inputs
IN : ANY Input value
Outputs
Q : INT Value converted to 16 bit integer
Remarks - For BOOL input data types, the output is 0 or 1. For REAL input data type, the output is the integer part of the input real. For TIME input data types, the result is the number of milliseconds. For STRING inputs, the output is the number represented by the string, or 0 if the string does not represent a valid number. In LD language, the conversion is executed only if the EN is TRUE. The ENO keeps the same value as the EN. In IL Language, the ANY_TO_INT function converts the current result.
ST Language
Q := ANY_TO_INT (IN) ;
FBD Language
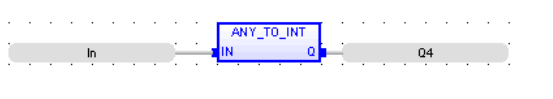
LD Language
(* The conversion is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO keeps the same value as EN *)

IL Language
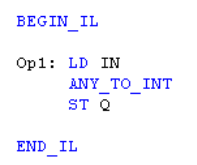
Return to the Top: Conversion Operations for IEC
Convert to UINT16
ANY TO UINT Unsigned Integer - [Data Type UINT] - A 16-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -0 (zero) to 65,535.
Unsigned Integer - [Data Type UINT] - A 16-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -0 (zero) to 65,535.
Operator - Converts the input into 16 bit unsigned integer value.
Inputs
IN : ANY Input value
Outputs
Q : INT Value converted to 16 bit unsigned integer
Remarks - For BOOL input data types, the output is 0 or 1. For REAL input data type, the output is the integer part of the input real. For TIME input data types, the result is the number of milliseconds. For STRING inputs, the output is the number represented by the string, or 0 if the string does not represent a valid number. In LD language, the conversion is executed only if the EN is TRUE. The ENO keeps the same value as the EN. In IL Language, the ANY_TO_UINT function converts the current result.
ST Language
Q := ANY_TO_UINT (IN) ;
FBD Language

LD Language
(* The conversion is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO keeps the same value as EN *)

IL Language

Return to the Top: Conversion Operations for IEC
Convert to INT32
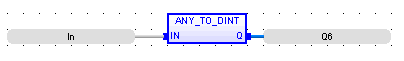
ANY TO DINT Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.
Double Integer - [Data Type DINT] - A 32-bit signed value. Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.
Operator - Converts the input into double integer value.
Inputs
IN : ANY Input value
Outputs
Q : Any Value converted to double interger
Remarks - For BOOL input data types, the output is 0 or 1. For REAL input data type, the output is the integer part of the input real. For TIME input data types, the result is the number of milliseconds. For STRING inputs, the output is the number represented by the string, or 0 if the string does not represent a valid number. In LD language, the conversion is executed only if the EN is TRUE. The ENO keeps the same value as the EN. In IL Language, the ANY_TO_DINT function converts the current result.
ST Language
Q := ANY_TO_DINT (IN) ;
FBD Language
LD Language
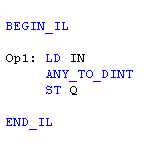
(* The conversion is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO keeps the same value as EN *)

IL Language
Return to the Top: Conversion Operations for IEC
Convert to UINT32
ANY TO UDINT Unsigned Double Integer - [Data Type UDINT] - A 32-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 4,294,967,296.
Unsigned Double Integer - [Data Type UDINT] - A 32-bit unsigned value. Unsigned Double Integers are used where the value of the data is expected to be in the range of 0 (zero) to 4,294,967,296.
Operator - Converts the input into unsigned double integer value.
Inputs
IN : ANY Input value
Outputs
Q : DINT Value converted to unsigned double integer
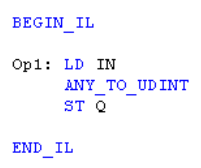
Remarks - For BOOL input data types, the output is 0 or 1. For REAL input data type, the output is the integer part of the input real. For TIME input data types, the result is the number of milliseconds. For STRING inputs, the output is the number represented by the string, or 0 if the string does not represent a valid number. In LD language, the conversion is executed only if the EN is TRUE. The ENO keeps the same value as the EN. In IL Language, the ANY_TO_UDINT function converts the current result.
ST Language
Q := ANY_TO_UDINT (IN) ;
FBD Language

LD Language
(* The conversion is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO keeps the same value as EN *)

IL Language
Return to the Top: Conversion Operations for IEC
Convert to REAL
Any To REAL REAL: Single precision floating point value - Real constant expressions must be valid number, and must include a dot ("."). If the user needs to enter a real expression having an integer value, add ".0" at the end of the number. The user can use "F" or "E" separators for specifying the exponent in case of a scientist representation. REAL is the default precision for floating points: such expressions do not need any prefix.
REAL: Single precision floating point value - Real constant expressions must be valid number, and must include a dot ("."). If the user needs to enter a real expression having an integer value, add ".0" at the end of the number. The user can use "F" or "E" separators for specifying the exponent in case of a scientist representation. REAL is the default precision for floating points: such expressions do not need any prefix.
Operator - Converts the input into real value
Inputs
IN : ANY Input value
Outputs
Q : REAL Value converted to real
Remarks - For BOOL input data types, the output is 0.0 or 1.0. For DINT input data type, the output is the same number. For TIME input data types, the result is the number of milliseconds. For STRING inputs, the output is the number represented by the string, or 0.0 if the string does not represent a valid number. In LD language, the conversion is executed only if the EN is TRUE. The ENO keeps the same value as the EN. In IL Language, the ANY_TO_REAL function converts the current result.
ST Language
Q := ANY_TO_REAL (IN) ;
FBD Language

LD Language
(* The conversion is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO keeps the same value as EN *)

IL Language

Return to the Top: Conversion Operations for IEC
Convert to STRING
Any To STRING String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.
String - [Data Type STRING] - A variable-length succession of characters. Each character is represented by one byte.
a. Cscape strings are delimited by the Single Quote character (').
b. Cscape strings may be zero characters in length.
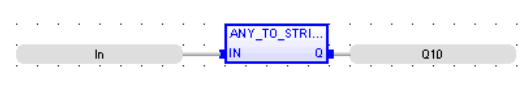
Operator - Converts the input into string value.
Inputs
IN : ANY Input value
Outputs
Q : STRING Value converted to string
Remarks - For BOOL input data types, the output is '1' or '0' for TRUE and FALSE respectively. For DINT, REAL or TIME input data types, the output is the string representation of the input number. This is a number of milliseconds for TIME inputs. In LD language, the conversion is executed only if the EN is TRUE. The ENO keeps the same value as the EN. In IL language, the ANY_TO_STRING function converts the current result.
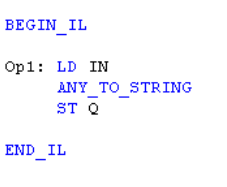
ST Language
Q := ANY_TO_STRING (IN) ;
FBD Language
LD Language
(* The conversion is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO keeps the same value as EN *)

IL Language
Return to the Top: Conversion Operations for IEC
Convert to TIME
Any To TIME TIME: Time of day - Time constant expressions represent durations that must be less than 24 hours. Expressions must be prefixed by either "TIME#" or "T#". They are expressed as a number of hours followed by "h", a number of minutes followed by "m", a number of seconds followed by "s", and a number of milliseconds followed by "ms". The order of units (hour, minutes, seconds, milliseconds) must be respected. The user cannot insert blank characters in the time expression. There must be at least one valid unit letter in the expression.
TIME: Time of day - Time constant expressions represent durations that must be less than 24 hours. Expressions must be prefixed by either "TIME#" or "T#". They are expressed as a number of hours followed by "h", a number of minutes followed by "m", a number of seconds followed by "s", and a number of milliseconds followed by "ms". The order of units (hour, minutes, seconds, milliseconds) must be respected. The user cannot insert blank characters in the time expression. There must be at least one valid unit letter in the expression.
Operator - Converts the input into time value.
Inputs
IN : ANY Input value
Outputs
Q : TIME Value converted to time
Remarks - For BOOL input data types, the output is t#0ms or t#1ms. For DINT or REAL input data type, the output is the time represented by the input number as a number of milliseconds. For STRING inputs, the output is the time represented by the string, or t#0ms if the string does not represent a valid time. In LD language, the conversion is executed only if the EN is TRUE. The ENO keeps the same value as the EN. In IL Language, the ANY_TO_TIME function converts the current result.
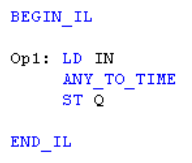
ST Language
Q := ANY_TO_TIME (IN) ;
FBD Language

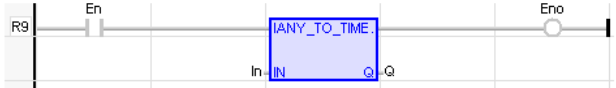
LD Language
(* The conversion is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO keeps the same value as EN *)
IL Language
Return to the Top: Conversion Operations for IEC
Any To LReal
Note: This block is supported only in Enhanced IEC Mode
Operator - Converts Any input into LReal value.
Inputs
IN : ANY Input value
Outputs
Q : Any Value converted to LReal
ST Language
Q := ANY_TO_LREAL (IN) ;
FBD Language

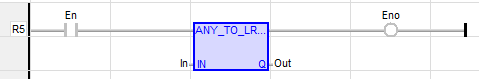
LD Language
(* The conversion is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO keeps the same value as EN *)
IL Language
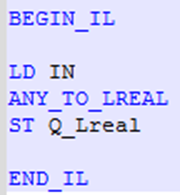
Return to the Top: Conversion Operations for IEC
Any To LINT
Note: This block is supported only in Enhanced IEC Mode
Operator - Converts Any input into LINT value.
Inputs
IN : ANY Input value
Outputs
Q : Any Value converted to LINT
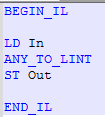
ST Language
Q := ANY_TO_LINT (IN) ;
FBD Language
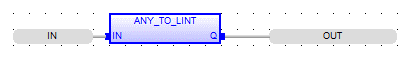
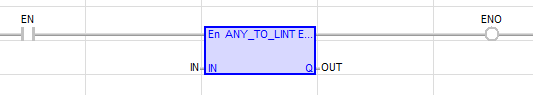
LD Language
(* The conversion is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO keeps the same value as EN *)
IL Language
Return to the Top: Conversion Operations for IEC
Any To ULINT
Note: This block is supported only in Enhanced IEC Mode
Operator - Converts Any input into ULINT value.
Inputs
IN : ANY Input value
Outputs
Q : Any Value converted to ULINT
ST Language
Q := ANY_TO_ULINT (IN) ;
FBD Language

LD Language
(* The conversion is executed only if EN is TRUE *)
(* ENO keeps the same value as EN *)

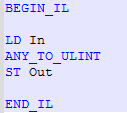
IL Language
Return to the Top: Conversion Operations for IEC