Boolean Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'. Operations for IEC
Boolean- [Data Type BOOL] - A single bit, binary value, or register/variable. Boolean points have only two possible values, 'TRUE' or 'FALSE'. Operations for IEC
See also: IEC 61131 Language Editor Programming
See also: Project Toolbox for IEC
Topic Menu
Home > View > Project Toolbox> Boolean Operations
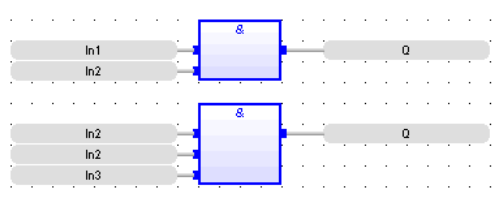
Boolean AND 
Operator - Performs a logical AND of all inputs.
Inputs
IN1 : BOOL First Boolean input
IN2 : BOOL Second Boolean input
Outputs
Q : BOOL Boolean AND of all inputs
Truth Table
| IN1 | IN2 | Q |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
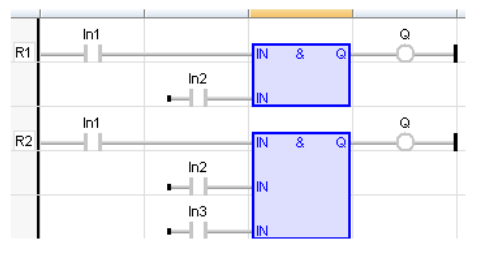
Remarks - In FBD language, the block may have up to 255 inputs. The block is called "&" in FBD language. In LD language, an AND operation is represented by serialized contacts. In IL language, the AND instruction performs a logical AND between the current result and the operand. The current result must be Boolean. The ANDN instruction performs an AND between the current result and the Boolean negation of the operand. In ST and IL languages, "&" can be used instead of "AND".
ST Language
Q : = IN1 AND IN2;
Q : = IN1 & IN2 & IN3;
FBD Language
(* the block may have up to 255 inputs *)
LD Language
IL Language

Return to the Top: Boolean Operations for IEC
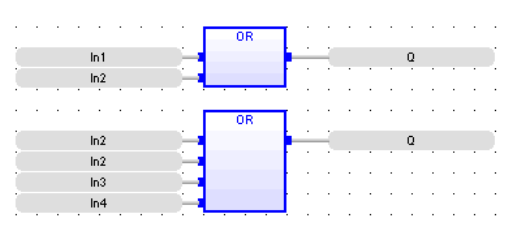
Boolean OR 
Operator - Performs a logical OR of all inputs.
Inputs
IN1 : BOOL First Boolean input
IN2 : BOOL Second Boolean input
Outputs
Q : BOOL Boolean OR of all inputs
Truth Table
| IN1 |
IN2 |
Q |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
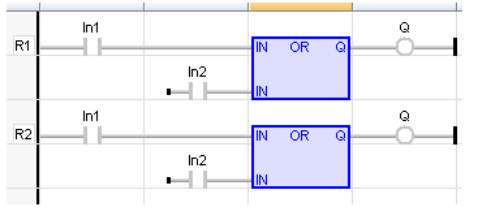
Remarks - In FBD language, the block may have up to 255 inputs. The block is called ">=1" in FBD language. In LD language, an OR operation is represented by contacts in parallel. In IL language, the OR instruction performs a logical OR between the current result and the operand. The current result must be Boolean. The ORN instruction performs an OR between the current result and the Boolean negation of the operand.
ST Language
Q : = IN1 OR IN2;
Q : = IN1 OR IN2 OR IN3;
FBD Language
(* the block may have up to 255 inputs *)
LD Language
IL Language

Return to the Top: Boolean Operations for IEC
Boolean XOR 
Operator - Performs an exclusive OR of all inputs.
Inputs
IN1 : BOOL First Boolean input
IN2 : BOOL Second Boolean input
Outputs
Q : BOOL Exclusive OR of all inputs
Truth Table
| IN1 | IN2 | Q |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Remarks - The block is called "=1" in FBD and LD languages. In IL language, the XOR instruction performs an exclusive OR between the current result and the operand. The current result must be Boolean. The XORN instruction performs an exclusive between the current result and the Boolean negation of the operand.
ST Language
Q := IN1 XOR IN2;
Q := IN1 XOR IN2 XOR IN3;
FBD Language
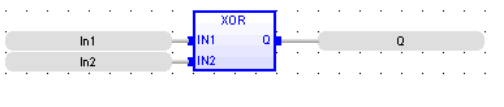
LD Language
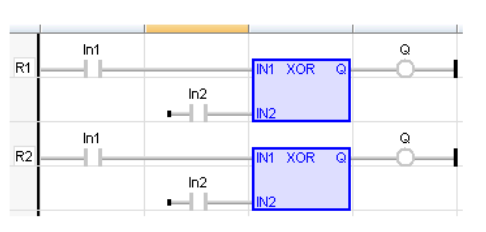
IL Language

Return to the Top: Boolean Operations for IEC
Boolean NOT 
Operator - Performs a Boolean negation of the input.
Inputs
IN : BOOL Boolean value
Outputs
Q : BOOL Boolean negation of the input
Truth Table
| IN | Q |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
Remarks - In FBD language, the block "NOT" can be used. Alternatively, the user can use a link terminated by a "o" negation. In LD language, negated contacts and coils can be used. In IL language, the "N" modifier can be used with instructions LD, AND, OR, XOR and ST. It represents a negation of the operand. In ST language, NOT can be followed by a complex Boolean expression between parenthesis.
ST Language
Q := NOT IN ;
Q := NOT (IN1 OR IN2) ;
FBD Language
(* explicit use of the "NOT" block *)
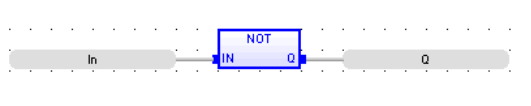
LD Language
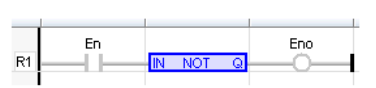
IL Language

Return to the Top: Boolean Operations for IEC
Rising Pulse Detection Also called: R_TRIG
Function Block - Rising pulse detection
Inputs
CLK : BOOL Boolean signal
Outputs
Q : BOOL TRUE when the input changes from FALSE to TRUE
Truth Table
| CLK | CLK prev | Q |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
ST Language
(* MyTrigger is declared as an instance of R_TRIG function block *)
MyTrigger (CLK);
Q := MyTrigger.Q;
FBD Language
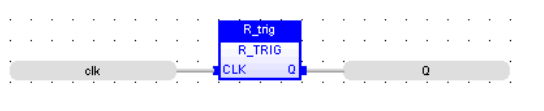
LD Language
(* The output signal is activated for one execution cycle, every time the input signal goes ON *)
(* the input signal is the rung - the rung is the output *)
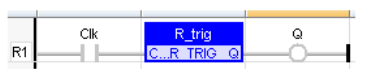
IL Language
(* MyTrigger is declared as an instance of R_TRIG function block *)
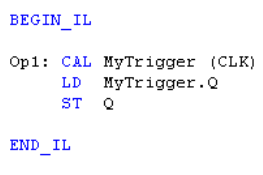
Return to the Top: Boolean Operations for IEC
Falling Pulse Detection
Function Block - Falling pulse detection
Inputs
CLK : BOOL Boolean signal
Outputs
Q : BOOLTRUE when the input changes from TRUE to FALSE
Truth Table
| CLK | CLK prev | Q |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
ST Language
(* MyTrigger is declared as an instance of F_TRIG function block *)
MyTrigger (CLK);
Q := MyTrigger.Q;
FBD Language
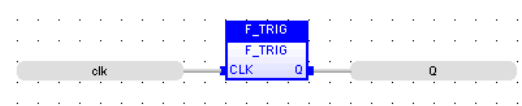
LD Language
(* The output signal is activated for one execution cycle, every time the input signal goes OFF *)
(* the input signal is the rung - the rung is the output *)
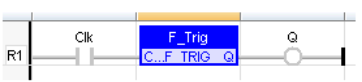
IL Language
(* MyTrigger is declared as an instance of F_TRIG function block *)

Return to the Top: Boolean Operations for IEC
Set Dominant Bistable
Function Block - Set dominant bistable.
Inputs
SET1 : BOOL Condition for forcing to TRUE (highest priority command)
RESET : BOOL Condition for forcing to FALSE
Outputs
Q1 : BOOL Output to be forced
Truth Table
| SET | RESET | Q1 prev | Q1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Remarks - The output is unchanged when both inputs are FALSE. When both inputs are TRUE, the output is forced to TRUE (set dominant).
ST Language
(* MySR is declared as an instance of SR function block *)
MySR (SET1, RESET);
Q1 := MySR.Q1;
FBD Language
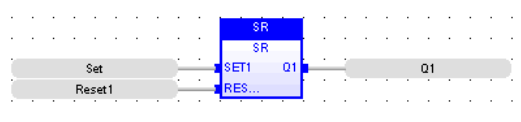
LD Language
(*SET command is the dominant command in case of both the commands being active simultaneously*)
(* the SET1 command is the rung - the rung is the output *)
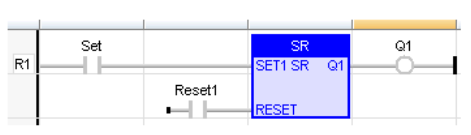
IL Language
(* MySR is declared as an instance of SR function block *)

Return to the Top: Boolean Operations for IEC
Reset Dominant Bistable
Function Block - Reset dominant bistable.
Inputs
SET : BOOL Condition for forcing to TRUE
RESET1 : BOOL Condition for forcing to FALSE (highest priority command)
Outputs
Q1 : BOOL Output to be forced
Truth Table
| SET | RESET1 | Q1 prev | Q1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Remarks - The output is unchanged when both inputs are FALSE. When both inputs are TRUE, the output is forced to FALSE (reset dominant).
ST Language
(* MyRS is declared as an instance of RS function block *)
MyRS (SET, RESET1);
Q1 := MyRS.Q1;
FBD Language
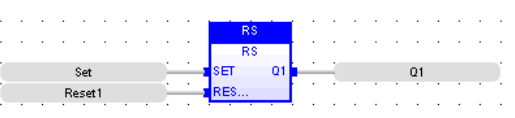
LD Language
(* RESET command is the dominant command in case of both the commands being active simultaneously*)
(* the SET command is the rung - the rung is the output *)
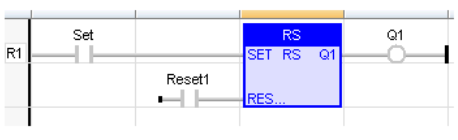
IL Language
(* MyRS is declared as an instance of RS function block *)

Return to the Top: Boolean Operations for IEC