FTP FTP - File Transfer Protocol - A standard Client/Server Internet protocol, based on RFC959, which supports file transfers over a TCP/IP network. Server Protocol
FTP - File Transfer Protocol - A standard Client/Server Internet protocol, based on RFC959, which supports file transfers over a TCP/IP network. Server Protocol
See also: Ethernet Configuration Overview
Topic Menu
FTP Server Protocol
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard Client/Server Internet protocol, based on RFC959, which supports efficient and reliable file transfers over a TCP/IP![]() TCP/IP – Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol - A transport layer protocol and a network layer protocol developed by the Department of Defense. This is a commonly used combination for communication within networks and across internetwork. network. In this context, the OCS acts as an FTP Server, which responds to file transfer requests from one or more FTP Clients.
TCP/IP – Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol - A transport layer protocol and a network layer protocol developed by the Department of Defense. This is a commonly used combination for communication within networks and across internetwork. network. In this context, the OCS acts as an FTP Server, which responds to file transfer requests from one or more FTP Clients.
Note: FTP protocol is supported only by OCS Models, which have built-in Ethernet and an OCS file system with removable media (such as Compact Flash/microSD). For OCS Models that do not have an OCS file system, the FTP (File Transfer) checkbox will be grayed out in Cscape’s Ethernet LAN1 Configuration dialog.
Note: This is a Non-Industrial Ethernet Protocol.
The OCS’s FTP Server supports both anonymous and authenticated file transfers between an FTP Client and the OCS file system. Authenticated file transfers require that the FTP Client provide one of two possible Username and Password pairs, before the OCS file system can be accessed. Properly authenticated, an FTP Client can access OCS file system functions, which include file read, file create, file delete, file rename, file write, directory read, directory create, and directory delete.
FTP Configuration
If FTP File Transfer will be used in the application, FTP Configuration must be performed, in addition to the general Ethernet LAN1 Configuration previously described in Ethernet Configuration Overview. To configure FTP protocol, use Cscape Programming Software to perform the following five steps:
-
Open the Ethernet LAN1 Configuration dialog by selecting Home > Controller > Hardware Configuration (select a series and device type) > LAN1/Config.
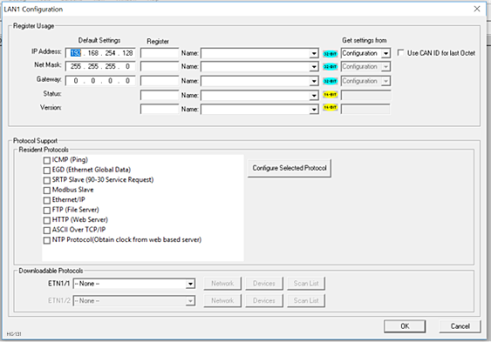
-
Enable FTP by checking the FTP (File Server) checkbox in the LAN1 Configuration dialog Until this is done, the OCS will not respond to any FTP Client requests.
-
Click on the Configure Selected Protocol button next to the FTP (File Server) checkbox to open the FTP Configuration dialog. Refer to figure below.
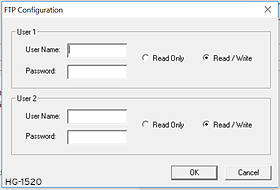
-
Optionally, set up the FTP Configuration parameters for User 1 and/or User 2 as follows:
Note: Usernames and Passwords are case-sensitive, and by default, Usernames and Passwords for both User 1 and User 2 are empty. In a typical application, both User 1 and User 2 should be configured - one with read-only access and the other with read-write access options are available.
-
Click OK to accept the new FTP protocol configuration.
Return to the Top: FTP Server Protocol
FTP Operation
After performing OCS FTP Configuration, a 3rd party FTP Client (such as a PC running SmartFTP) can be used to access the OCS file system. The target OCS’s configured IP Address, FTP username (if any), and FTP Password (if any), must be entered into the FTP Client, to establish an FTP connection before any file accesses can be initiated. Please refer to documentation provided with the 3rd party FTP Client, regarding how to install, configure and operate the FTP Client. When configuring an FTP Client, the user should be aware that the FTP protocol standard defines many optional features. Like many UNIX implementations, the OCS FTP Server imposes constraints on some of these options, as shown in table below.
In addition, since the FTP Server will automatically disconnect an FTP Client after about 3 minutes of inactivity, the user might need to configure the FTP Client to periodically send NOOP (No Operation) commands to the FTP Server, to keep the connection alive.
FTP File Accessing
When using FTP to exchange files with an OCS, the user should know that the OCS file system implements an “8.3” filename format, which means all file and directory names should consist of up to 8 characters, followed by an optional dot, and an optional extension with up to 3 characters. Also, the OCS file system allows multiple concurrent file accessing. For example, an FTP Client can read a file at the same time the OCS ladder program is logging data to another file. It is also possible for both the FTP Client and OCS ladder functions to read the same file at the same time. If there is a file access conflict, such as an FTP Client attempting to delete a file that is currently being read or written by ladder, the file delete request is denied and an error response is sent to the FTP Client.
Return to the Top: FTP Server Protocol