SNP Protocol
See also: Help for Serial Protocols
SNP ID
When the SNP ID is entered, a six digit ID with leading zeros is created. For example if the ID “12” is entered, the SNP ID in your device should be set to “000012”. Entering an ID of “0” will create a NULL SNP ID where all six ID characters should be set to NULL.
CSCAPE Configuration
To configure OCS for the SNP protocol, select the Protocol Configuration from the Program menu in CSCAPE software. Select the appropriate protocol type in desired port. To make sure that the Software is able to configure the equipment for the correct protocol, make sure Snp.dll file is in the Protocols directory of the current working/open Cscape.
Configuring GE SNP Device
Following are the steps for configuring GE SNP with Cscape application:
Open Program > Protocol Config and perform the following configurations:
Step 1: Select GE SNP (Series 90 Protocol) from the drop-down list.
Step 2: On network configuration dialog user can configure following network parameters/status registers.
-
Configure Baud Rate, Parity, Stop Bits, Handshake, Protocol (SNP), RS-232/485, Retries and Timeout.
-
Configure the update Scan type as automatic or manual according to process requirements.
-
Configure the (optional/recommended) network status register.
Step 3: Click Devices button to configure Slave device (0-255) as follows:
Configure slave device name and ID.
If option for Swap Words on 32-bit Data is checked, the high and low 16-bit values of 32-bit Data are swapped when transferred between the target and OCS.
Device status registers can be optionally enabled and used to determine the current state of communications.
Select Stop on Error or Retry on Error as per process requirement.
Step 4: Click Scan List button to configure Data Mapping.
-
To transfer data between the OCS and remote target, a Scan List must be created that defines each transaction. Each mapping entry (transaction) contains the source and destination registers, the number of consecutive registers transferred, the direction of the transfer and trigger for transfer (optional).
Entering Registers
Registers should be entered with the “%” prefix, the type should be in uppercase and the type and range should follow the chart below.
| REGISTER | Type | Start | End |
|---|---|---|---|
|
DATA |
%R |
1 |
16384 |
|
RELAY |
%M |
1 |
32768 |
|
INPUT |
%I |
1 |
32768 |
|
OUTPUT |
%Q |
1 |
32768 |
|
TEMPORARY |
%T |
1 |
512 |
|
ANALOG INPUTS |
%AI |
1 |
8192 |
|
ANALOG OUTPUTS |
%AQ |
1 |
8192 |
|
DISCRETE SA |
%SA |
1 |
256 |
|
DISCRETE SB |
%SB |
1 |
256 |
|
DISCRETE SC |
%SC |
1 |
256 |
|
DISCRETE S |
%S |
1 |
256 |
|
GENIUS GLOBALS |
%G |
1 |
7680 |
Network Communication Errors
In order to access the Network statistics, user must assign the “Network status register” in network configuration. The table below gives the details of statistics.
| Number | Statistics | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
Update interval exceeded count |
%Rx |
This register explains number of times that the actual transaction scan time to complete all transactions exceeded specified update interval. Generally used as an indicator that an excessive number of triggered transfers or failed communication retries are occurring that is lengthening the expected transaction scan time.
If the Update interval is set to zero (update as fast as possible), this 32-bit register alternately specifies the actual transaction scan time in mSec resolution. |
|
2 |
No response count |
%R(x+2) |
This register explains number of times that a device(s) did not respond to a transaction. This includes ALL failed transaction, not just those after the retry count is exceeded. |
|
3 |
Corrupt Response Count |
%R(x+4) |
This register explains number of times that a device(s) returned an invalid or failed response to a transaction. This includes ALL failed.
Transaction, not just those after the retry count is exceeded. |
|
4 |
Valid Response Count |
%R(x+6) |
This register explains total number of valid responses. |
NOTE: %Rx: 32-bit network status register configured in Network configuration. For example: %R500(501).
Device Communication Errors
| Error | Error Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
INVALID_BLOCK |
-203 |
Invalid size for data type. |
|
NO_RESPONSE_FROM_PLC |
-204 |
Timeout while waiting for remote node response. |
|
INVALID_RESPONSE_FROM_PLC |
-205 |
Corrupted response from remote node. |
|
INVALID_INITIALISATION |
-207 |
Internal Error - Unable to open port. |
Connection Details
Illustrations below show the various end-of-cable connectors required:
| 25-Pin D-Type Male | 10-Pin Weidmuller
Cage Clamp |
8-Pin RJ 45 Plug | 9-Pin DB Male |
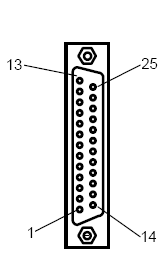
|

|
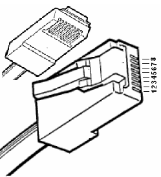
|
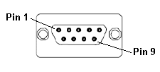
|
| CN1 | CN1 | MJ1/MJ2 | Port 1 |
Half-Duplex RS422 Mode
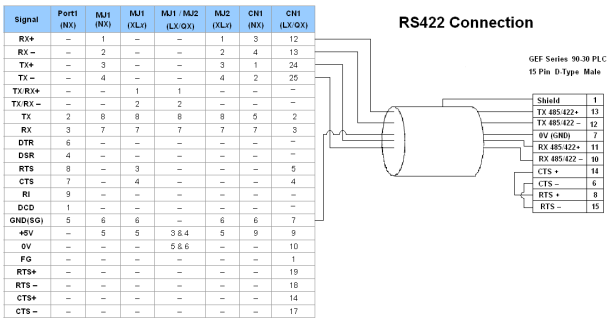
Port 1 — DB9 (Female at OCS end)
MJ1/MJ2 — RJ45 (Female at OCS end)
CN1 — 10-Pin Weidmuller Cage Clamp (Female at OCS end)
CN1 — DB25 (Female at OCS end)
NOTES:
-
Do not connect to unlisted pins.
-
Recommended Cable: Beldon 9503, twisted multipair, screened.
-
Connect the screens together at the shield / earth pin of the PLC.
Full-Duplex RS422 Mode
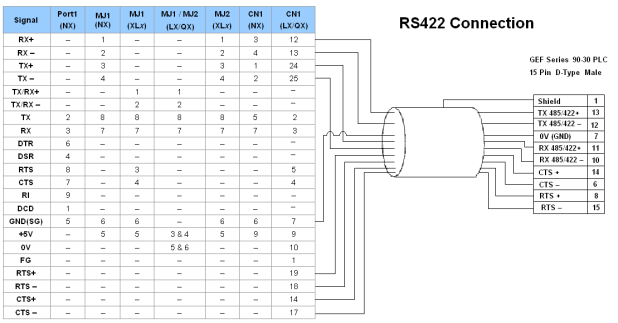
Port 1 — DB9 (Female at OCS end)
MJ1/MJ2 — RJ45 (Female at OCS end)
CN1 — 10-Pin Weidmuller Cage Clamp (Female at OCS end)
CN1 — DB25 (Female at OCS end)
NOTES:
-
Do not connect to unlisted pins.
-
Recommended Cable: Beldon 9503, twisted multipair, screened.
-
Connect the screens together at the shield / earth pin of the PLC.